Report Highlights. The average cost of college tuition & fees at public 4-year institutions* has risen 141.0% over the last 20 years for an average annual increase of 7.0%.
- Between the 2021-22 and 2022-23 academic years, tuition at the average public 4-year institution increased 1.6%.
- In the 21st Century, the rising costs of college have outpaced the rate of inflation by an average of 104.3% and by as much as 2,217% (2015).
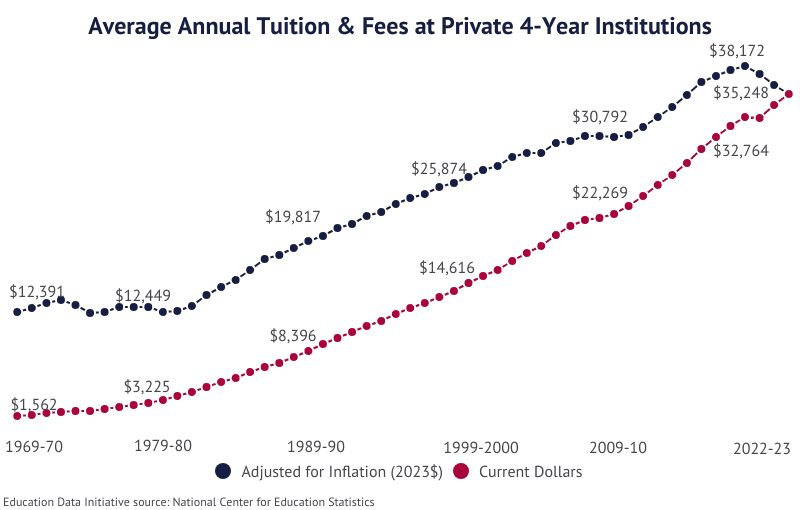
- The average cost of tuition & fees at private 4-year institutions has risen 181.3% over the last 20 years for an average annual increase of 5.5%.
- Since 1989-90, average tuition and fee rates have increased 181.3% after adjusting for inflation.
- In the last 55 years, the 1972-73 academic year saw the largest year-over-year (YoY) tuition growth rate at 17.5%.
*The term “college” in this report generally refers to public 4-year institutions unless otherwise noted.
Jump to a decade: 1920s | 1930s | 1940s | 1950s | 1960s | 1970s | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s
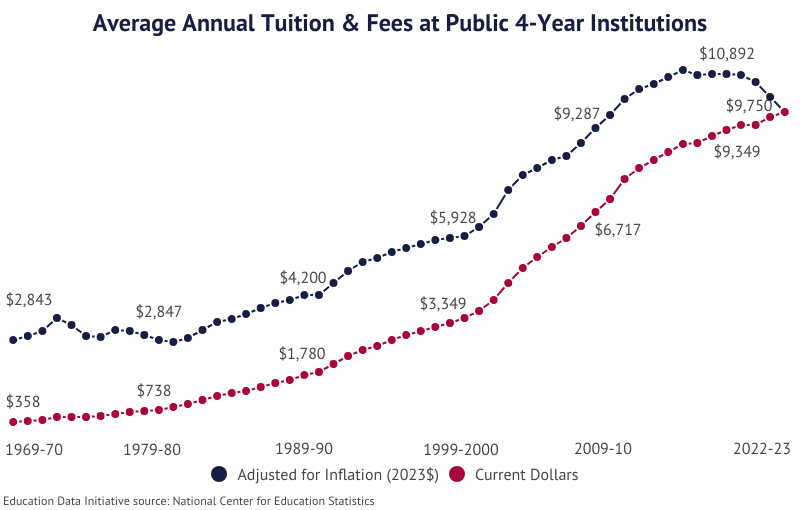
| Year | Public 4-Year | Private 4-Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-23 | $9,750 | $35,248 |
| 2021-22 | $9,596 | $34,051 |
| 2020-21 | $9,374 | $32,728 |
| 2019-20 | $9,349 | $32,769 |
| 2018-19 | $9,212 | $31,883 |
| 2017-18 | $9,036 | $30,723 |
| 2016-17 | $8,804 | $29,476 |
| 2015-16 | $8,778 | $27,942 |
| 2014-15 | $8,543 | $26,739 |
| 2013-14 | $8,312 | $25,707 |
| 2012-13 | $8,070 | $24,523 |
| 2011-12 | $7,713 | $23,464 |
| 2010-11 | $7,132 | $22,677 |
| 2009-10 | $6,717 | $22,269 |
| 2008-09 | $6,312 | $22,040 |
| 2007-08 | $5,943 | $21,427 |
| 2006-07 | $5,666 | $20,517 |
| 2005-06 | $5,351 | $19,292 |
| 2004-05 | $5,027 | $18,604 |
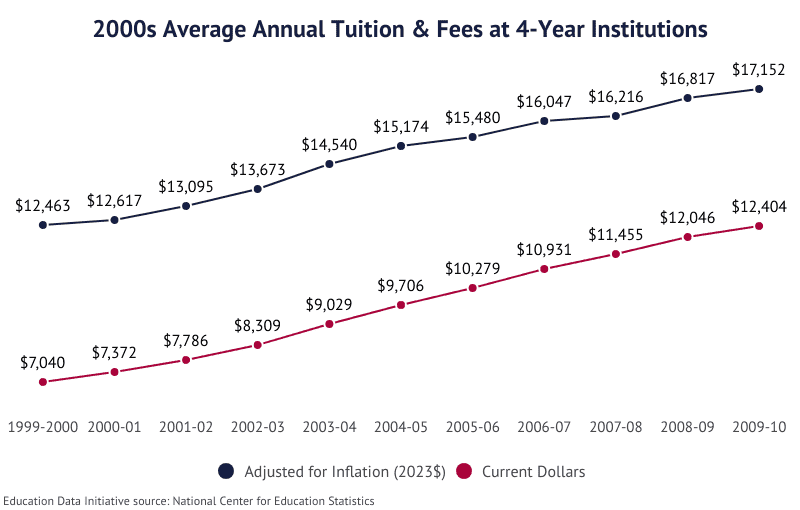
| 2003-04 | $4,587 | $17,763 |
| 2002-03 | $4,046 | $16,826 |
| 2001-02 | $3,735 | $16,211 |
| 2000-01 | $3,501 | $15,470 |
| 1999-2000 | $3,349 | $14,616 |
| 1998-99 | $3,229 | $13,973 |
| 1997-98 | $3,110 | $13,344 |
| 1996-97 | $2,987 | $12,881 |
| 1995-96 | $2,848 | $12,243 |
| 1994-95 | $2,681 | $11,481 |
| 1993-94 | $2,537 | $10,952 |
| 1992-93 | $2,349 | $10,294 |
| 1991-92 | $2,117 | $9,759 |
| 1990-91 | $1,888 | $9,083 |
| 1989-90 | $1,780 | $8,396 |
| 1988-89 | $1,646 | $7,722 |
| 1987-88 | $1,537 | $7,116 |
| 1986-87 | $1,414 | $6,658 |
| 1985-86 | $1,318 | $6,121 |
| 1984-85 | $1,228 | $5,556 |
| 1983-84 | $1,148 | $5,093 |
| 1982-83 | $1,031 | $4,639 |
| 1981-82 | $909 | $4,113 |
| 1980-81 | $804 | $3,617 |
| 1979-80 | $738 | $3,225 |
| 1978-79 | $688 | $2,958 |
| 1977-78 | $655 | $2,700 |
| 1976-77 | $617 | $2,534 |
| 1975-76 | $542 | $2,291 |
| 1974-75 | $512 | $2,130 |
| 1973-74 | $514 | $2,045 |
| 1972-73 | $503 | $1,948 |
| 1971-72 | $428 | $1,832 |
| 1970-71 | $394 | $1,706 |
| 1969-70 | $358 | $1,562 |
| 1968-69 | $321 | $1,417 |
| 1967-68 | $310 | Unavailable |
| 1966-67 | $302 | Unavailable |
| 1965-66 | Unavailable | Unavailable |
| 1964-65 | Unavailable | Unavailable |
| 1963-64 | $243 | $1,011 |
Related reports include: Average Cost of College & Tuition | Average Student Loan Debt by Year | Student Loan Debt Crisis | Average Cost of Private School | Average Cost of Community College
Average Annual Cost of College
Most financial experts attribute he sudden increases that started in the 1970s with an influx of federal funding designed to make college more affordable.
- Postsecondary institutions raise tuition (and fees) an average 5.87% each year.
- For the 2022-23 academic year, colleges increased tuition 2.67%.
- Public 4-year institutions raised tuition 1.60%.
- Private nonprofit 4-year colleges raised tuition 3.21%.
- Private for-profit institutions raised tuition 2.34%.
- Ivy League University of Pennsylvania* (U-Penn) raised annual undergraduate tuition and fees 4.18% for the 2023-24 academic year.
- For every $1 received by higher learning institutions in subsidized federal student loans, college tuition increases by $0.60.
- The average cost of attendance for one academic year at any postsecondary institution is $27,673.
- Tuition and fees total $14,688.
- Student housing and meal plans average $7,337 and $5,649, respectively.
- Among 4-year institutions, annual tuition and fees total $17,709.
- Public 4-year institutions charge $9,750 per year.
- Federal support for postsecondary education amounted to $174.9 billion in 2021; the 2022 budget of $577.5 billion included funding for the CARES Act.
- An additional $83.6 billion comes from off-budget and non-federal support, most of which goes toward student financial aid.
- An additional $84.8 billion comes from off-budget and non-federal support, most of which goes toward student financial aid.
*The University of Pennsylvania is a private research university that keeps meticulous records pre-dating the dawn of the 20th Century.
Average Cost of College in the 21st Century
The latest data indicates that escalation of academic costs may be slowing down, possibly below some YoY growth rates from the 1960s.
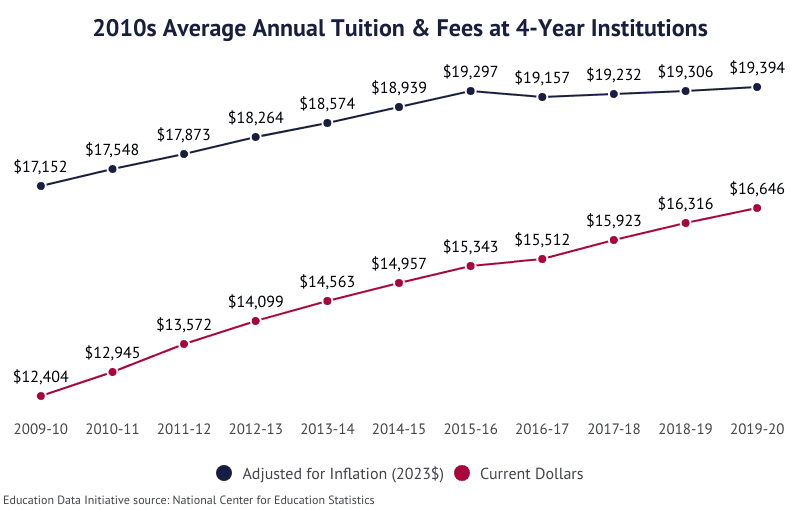
- Between 2009-10 and 2022-23, the total cost of attendance (fees, tuition, room, and board) saw an increase of 48.9% at public 4-year schools.
- At private 4-year schools, costs grew 55.9%.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2009-10, the cost of attendance at nonprofit private institutions grew from $20,989 per year to $34,920, an annual growth rate of 5.2%.
- During the same period, for-profit private institutions increased the cost of attendance from $16,124 to $24,118, a 4.1% annual growth rate.
- From 2009-10 to 2019-20, private nonprofits increased costs to $48,815, an annual growth rate of 3.4%.
- In the same period, private for-profits increased costs to $27,561, growing at an annual rate of 1.3%.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2019-20, tuition at the average 4-year institution increased 136.5%, an annual rate of 4.4%.
- Tuition and fees in the 1990s increased 73%.
- From 1963-64 to 1968-69, academic costs increased at an average annual rate of 3.25%; that’s 19.3% faster than the increase between the 2021-22 and 2022-23 academic years.
- Federal funding budgeted for postsecondary education totaled $23.0 billion in 2000.
- In 2010, the budget increased to $58.2 billion, an annual growth rate of 9.73% from 2000.
- In 2019, the budget was $107.5 billion, an annual growth rate of 7.06% from 2010.
- In 2020 and 2021, the budget was $213.5 billion and $236.8 billion, respectively.
- Including all off-budget and non-federal funding, federally-mandated costs for postsecondary education increased at an average annual rate of 2.5% from 2010 to 2019.
- Federally mandated costs for postsecondary education increased 86.4% per year from 2010 to 2022; this growth rate is heavily inflated by funding for the CARES Act.
Average Cost of College in the 20th Century
When the century began, many colleges were very low cost and some were free. After student financial aid became commonplace, college costs escalated beyond those of any other industry.
- In 1900, undergraduates paid $150 to attend the University of Pennsylvania and its Wharton School.
- By 1913, the annual cost to undergraduates increased to $160; this is a 0.50% average annual growth rate.
- In 1999, undergraduates paid $24,230 to attend U-Penn.
- After adjusting for inflation, the cost of a year as an undergraduate at U-Penn increased 803.3% between 1913 and 1999; this is a 2.6% average annual growth rate.
- Between the 1969-70 academic year to 1999-2000, the national average cost of tuition and fees at the average 4-year institution increased 832.5%.
- After adjusting for inflation, the annual growth rate of tuition between 1969 and 1999 was 2.47%.
- The 1981-82 academic year saw the century’s largest rise in tuition over the previous year (up 13.0%).
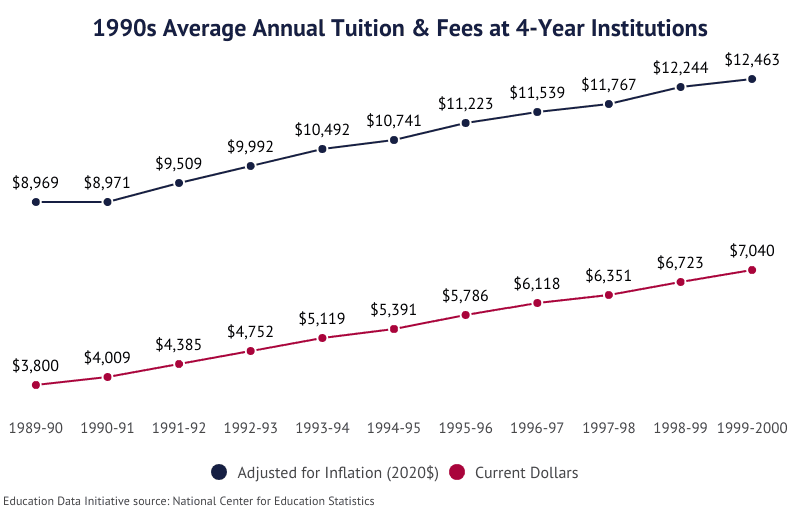
College Costs in the 1990s
The 1990s saw the rise of the for-profit college, which took advantage of federal funding programs. While such institutions charged less for attendance than their nonprofit counterparts, they would become notorious for hidden expenses, poor instruction, and fraud.
- In the 1989-90 academic year, tuition at the average public 4-year institution was $1,780.
- In 1999-2000, tuition at a public 4-year institution averaged $3,349; this is an average annual growth rate of 6.52%.
- Between 1989-90 and 1999-2000, the total cost of attendance (fees, tuition, room, and board) increased 66.3% at public 4-year schools, from $4,975 to $8,274.
- At private 4-year schools, the cost of tuition grew 74.1%, from $8,396 to $14,616.
- In that same period, the cost of attendance at a private 4-year institution increased from $12,284 to $20,737, an annual growth rate of 5.38%.
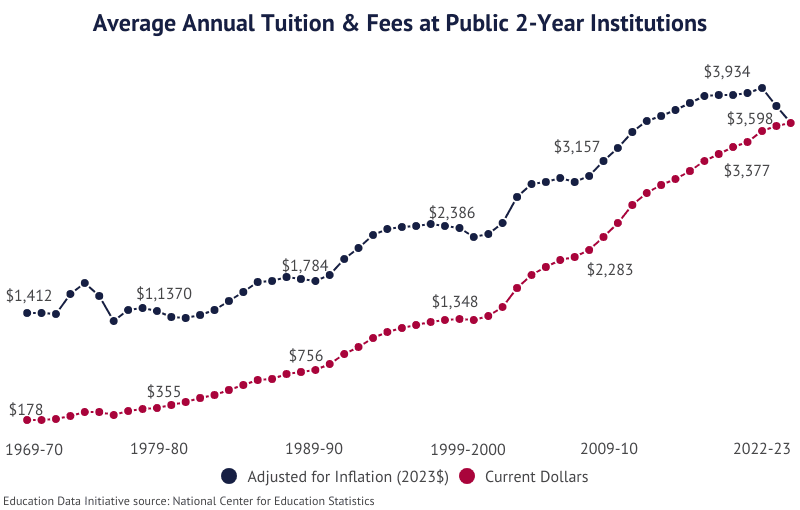
- Tuition at the average public 2-year institution increased from $756 to $1,348, an annual growth rate of 5.95%.
- Tuition at the average private 2-year institution increased 58.3%, from $5,196 to $8,225.
- Among all postsecondary institutions, the cost of tuition increased at an average annual rate of 6.28%.
- After adjusting dollar values for inflation, costs increased at an average annual rate of 3.30%.
- The largest YoY average tuition increase was 8.95% between the 1990-91 and 1991-92 academic years.
- After adjusting for inflation, the 1993-94 academic year saw a 6.07% increase in tuition over the previous year.
- The federal budget for postsecondary education amounted to $18.1 billion in 1990.
- Throughout the decade, the federal budget increased 27.3%.
- If off-budget and nonfederal funds generated by federal legislation (most of which funded student loans) are included, total federal spending increased 86.1%.
- Funding for FFEL loans increased by $11.9 billion or 110%.
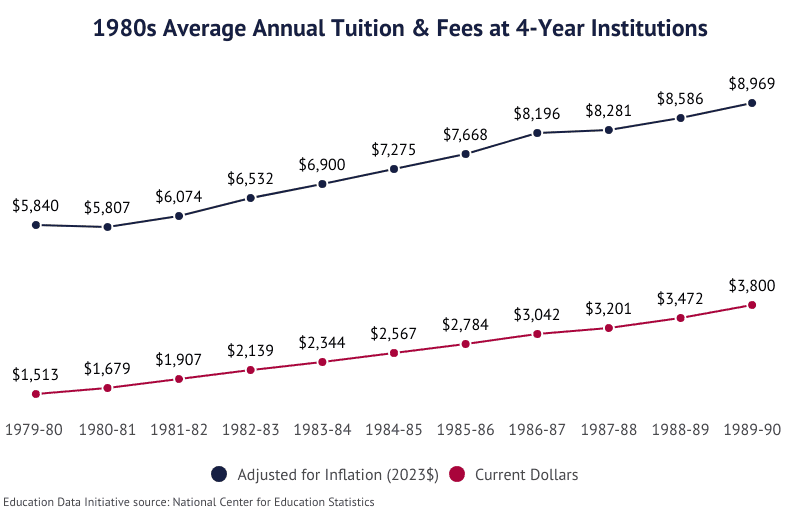
College Costs in the 1980s
Public investment in high education dropped as college students and their familes began borrowing at never before seen rates.
- In the 1979-80 academic year, the average annual cost of tuition and fees at public 4-year institutions was $738.
- By 1989-90, annual tution and fees averaged $1,780, a 9.2% average annual growth rate.
- Between 1979-80 and 1989-90, the total cost of attendance (fees, tuition, room, and board) saw an increase of 113.8% at public 4-year schools, from $2,327 to $4,975.
- At private 4-year schools, tuition grew 160.3%, from $3,225 to $8,396.
- Between 1979-80 and 1989-90, the cost of attendance at private 4-year institutions grew from $5,013 per year to $12,284, an annual growth rate of 9.38%.
- Tuition at the average public 2-year institution increased from $355 to $756, an annual growth rate of 7.85%.
- Tuition at the average private 2-year institution increased 152.0%, from $2,062 to $5,196.
- The federal budget for postsecondary education amounted to $11.09 billion in 1980.
- Throughout the decade, the federal budget increased 62.9%.
- If off-budget and nonfederal funds generated by federal legislation (most of which funded student loans) are included, total federal spending increased 94.5%.
- Funding for FFEL loans increased by $6.23 billion or 135.5%.
- The most dramatic increase in costs to all postsecondary students was between the academic years of 1980-81 and 1981-82, when the average cost of attendance at any postsecondary institution grew 12.5%; that is:
- 33.4% faster than the rate of inflation at the time (which was 8.92%).
- 96.6% faster than academic inflation in the first decade of the 20th century (4.36%).
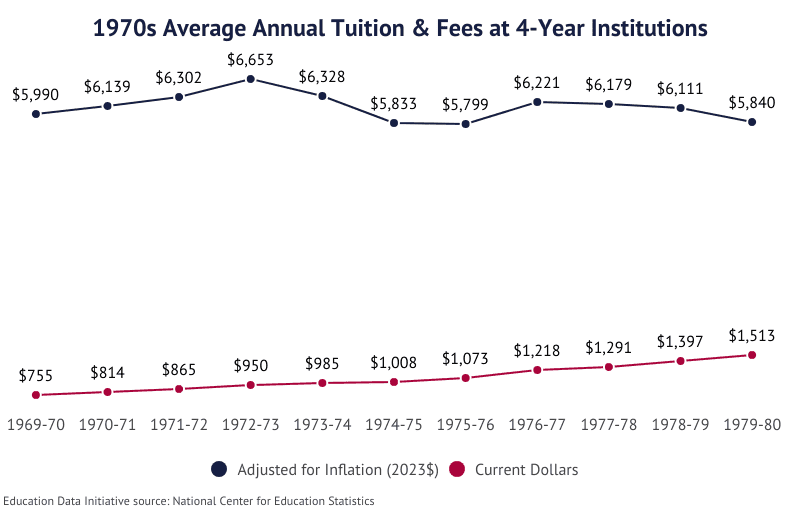
College Costs in the 1970s
A new national recession began, and federal student loans became commonplace. The average cost of tuition and fees at 4-year institutions doubled.
- Between 1969-70 and 1979-80, the cost of tuition and fees at the average public 4-year institution increased from $358 to $738, an average annual increase of 7.5%.
- The total cost of attendance (fees, tuition, room, and board) saw an increase of 88.0% at public 4-year schools, from $1,238 to $2,327.
- During that same period, tuition at private 4-year institutions grew from $1,562 to $3,225, an annual growth rate of 7.52%.
- The cost of attendance grew 95.9%, from $2,559 to $5,013.
- Tuition at the average public 2-year institution increased from $178 to $355, an annual growth rate of 7.15%.
- Tuition at the average private 2-year institution increased 99.4%, from $1,034 to $2,062.
- The federal budget for postsecondary education amounted to $3.43 billion in 1970.
- Throughout the decade, the federal budget increased 223%.
- If off-budget and nonfederal funds generated by federal legislation (most of which funded student loans) are included, total federal spending increased 210%.
- Funding for FFEL loans increased by $3.83 billion or 497%.
College Costs in the 1960s
In 1965, the Higher Education Act was passed to help make college more affordable through financial aid from the government to students. Most federal data dates to the 1963-64 academic year.
- In the 1960s, the average cost of tuition and fees at any 4-year college increased at an annual rate of 5.33%.
- The average cost of attendance at any postsecondary institution grew at an annual rate of 4.06%.
- In the 1963-64 academic year, tuition and fees at the average public 4-year university totaled $243 annually.
- The cost of tuition and fees increased to $358 for 1969-70.
- Between 1963-64 and 1969-70, the cost of tution and fees at the average public 4-year institution increased 47.3%, growing at an annual rate of 6.67%.
- During this same period, the total cost of attendance (fees, tuition, room, and board) saw an increase of 33.3% at public 4-year schools.
- Between 1963-64 and 1969-70, the cost of attendance at private institutions grew from $1,815 per year to $2,527, an annual growth rate of 5.94%.
- During this same period, tuition at the average 2-year institution increased 44.4%, an annual rate of 6.32%.
- Tuition at the average public 2-year institution increased from $97 to $178, an annual growth rate of 10.6%.
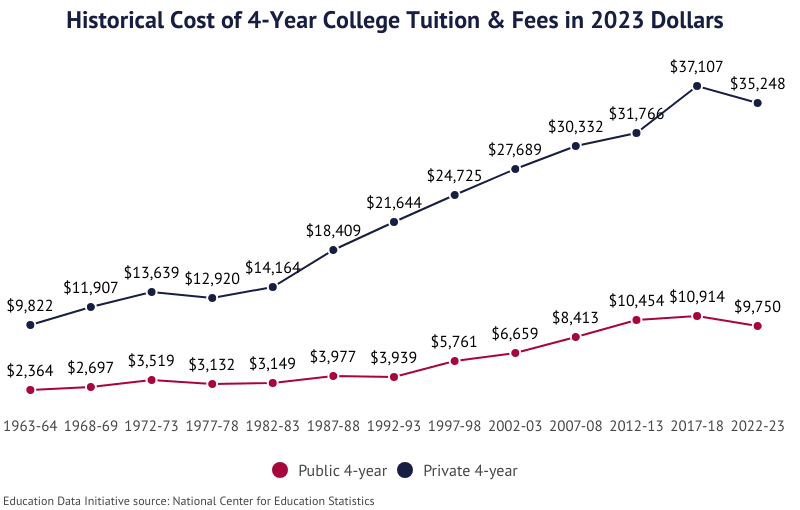
College Costs in the 1950s
Official data from 1950 or earlier is, for the most part, unavailable. Some institutions, such as the University of Pennsylvania, maintain archives of such information.
- In 1950, the U-Penn charged undergraduates $625 for the academic year.
- In 1959, the annual cost totaled $1,400.
- Throughout the decade, college costs rose 124% to the equivalent of $14,889 in January 2024 dollars.
- Undergraduates attending U-Penn in the 2023-24 academic year will pay $66,104, a 337.3% increase over 1959 equivalent costs (that is, $15,115 in January 2024 dollars).
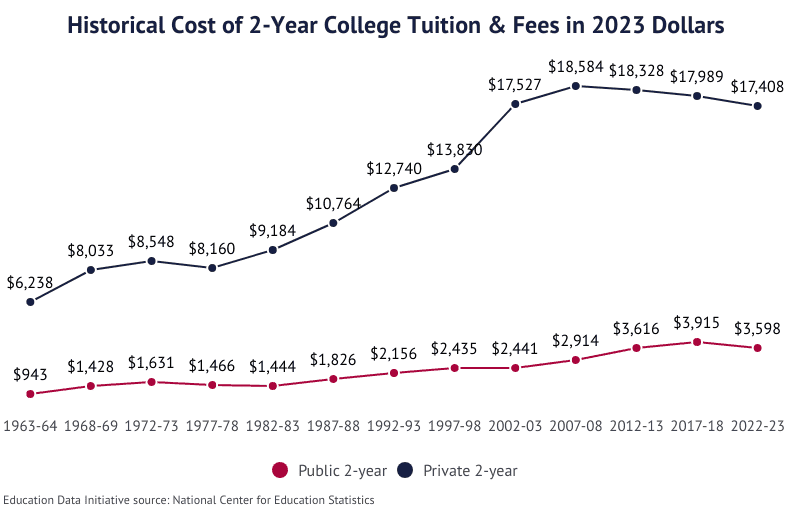
College Costs in the 1940s
Tuition was still relatively affordable for most households, and the first federal student aid program began.
- The 1944, the Servicemen’s Readjustment Act, also known as the GI Bill, provided federal aid for tuition, fees, and other educational expenses for veterans.
- Veterans would receive a free year of college, $500 in tuition, and monthly living allowance while studying.
- Under the GI Bill, post-war enrollment surged 10 times higher what had been anticipated.
- In 1947, veterans accounted for nearly half of college admissions.
- Also in 1947, the cost to attend Harvard university was $525.
- One year of Harvard attendance cost the equivalent of 17.5% of the average household income ($3,000).
- Comparatively, attending Harvard for a year in 2011 cost $34,976, equivalent to 69.9% of the nationwide median household income.
- By 2014, the cost to attend Harvard was $38,891, 72.5% of the national median household income.
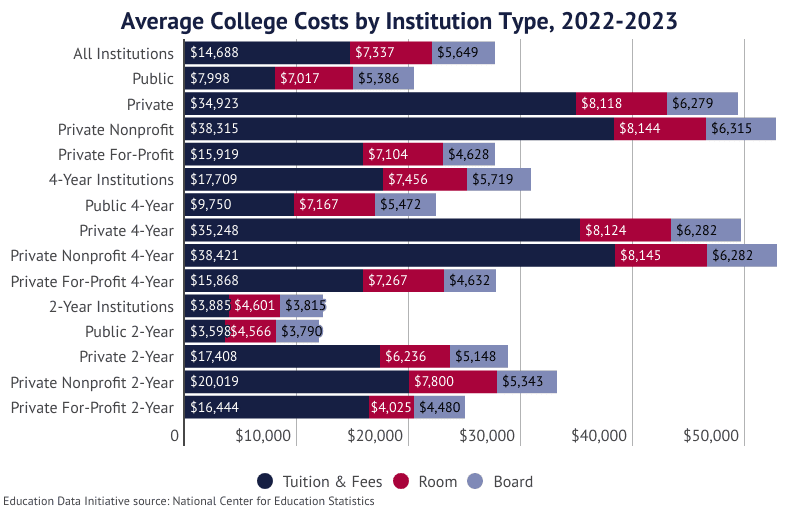
College Costs in the 1930s
Through the height of the Great Depression, some postsecondary institutions kept costs low to account for students’ presumably reduced income.
- In 1930, first-year undergraduates paid $400 to attend the University of Pennsylvania.
- In 1939, the cost of attendance at the University of Pennsylvania increased to $420.
- In 1934, the cost of attendance for first-year students at Dartmouth was $1,700, or $40,462 in January 2024 dollars.
- Dartmouth estimates the cost of attendance for 2024-25 to be $90,813.
- Dartmouth’s tuition increased at an average rate of 4.52% per year over the last 90 years.
- Adjusting for inflation, tuition values increase 0.90% per year.
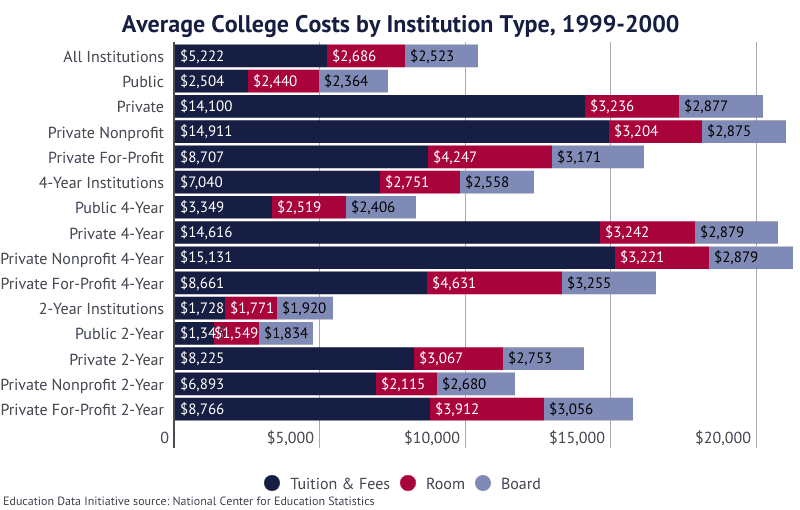
College Costs in the 1920s
Discharged World War I veterans packed postsecondary schools in the ’20s. At the University of Washington, enrollment grew from 3,000 in 1918 to 8,500 in 1931. There was no tuition assistance for veterans in this era.
- In 1920, Stanford charged $120 ($1,953 in 2024 dollars) per year.
- At the University of Pennsylvania, the annual cost of tuition and fees for a first-year undergraduate was $270.
- In 1929, first-year students at U-Penn paid $400, a 48.1% increase.
- For the average student, the year’s textbooks totaled between $30 and $35.
- Throughout the decade, the cost of room and board increased from $350 to $520.
- Including all costs, college freshman in 1929 paid a total of $170 more than at the start of the decade, a 48.6% increase.
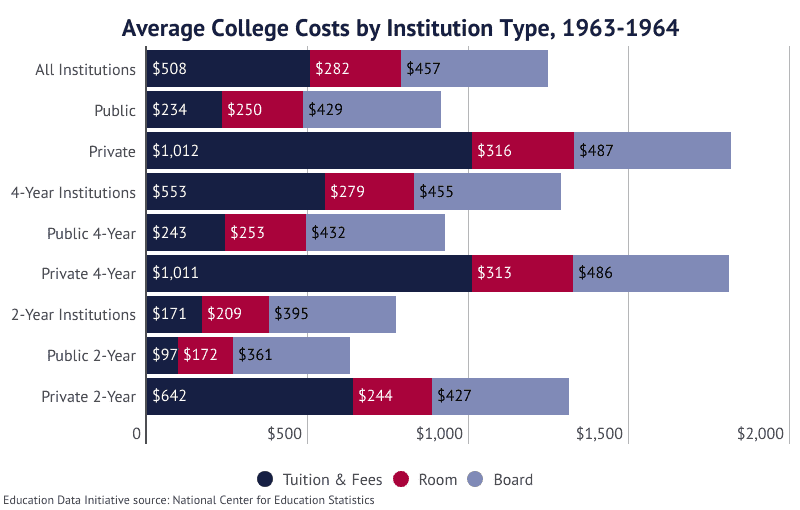
| Year (Fall) | Nonprofit 4-Year | For-Profit 4-Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-23 | $38,421 | $15,868 |
| 2021-22 | $37,225 | $15,505 |
| 2020-21 | $35,852 | $15,400 |
| 2019-20 | $35,799 | $14,957 |
| 2018-19 | $34,770 | $14,715 |
| 2017-18 | $33,748 | $14,677 |
| 2016-17 | $32,717 | $14,423 |
| 2015-16 | $31,578 | $14,150 |
| 2014-15 | $30,789 | $13,924 |
| 2013-14 | $29,823 | $13,714 |
| 2012-13 | $28,743 | $13,691 |
| 2011-12 | $27,616 | $13,712 |
| 2010-11 | $26,581 | $13,727 |
| 2009-10 | $25,535 | $13,769 |
| 2008-09 | $24,636 | $14,423 |
| 2007-08 | $23,328 | $14,644 |
| 2006-07 | $21,994 | $14,593 |
| 2005-06 | $20,732 | $13,315 |
| 2004-05 | $19,652 | $13,197 |
| 2003-04 | $18,584 | $12,398 |
| 2002-03 | $17,517 | $11,407 |
| 2001-02 | $16,604 | $11,069 |
| 2000-01 | $15,811 | $10,411 |
| 1999-2000 | $15,131 | $8,661 |
| Year (Fall) | Nonprofit (& For-Profit) 4-Year* | |
| 1998 | $13,973 | |
| 1997 | $13,344 | |
| 1996 | $12,881 | |
| 1995 | $12,243 | |
| 1994 | $11,481 | |
*For-profit colleges did not become prevalent until the late ’90s.
Public vs. Private College Costs
Private colleges and universities receive no institutional funding from federal or state governments.
- Annual tuition at the average private institution is $34,923.
- Average tuition at private institutions is 125.5% higher than tuition at public institutions.
- Private nonprofit institutions charge 82.6% more in tutition than private for-profit institutions.
- In the 21st century, annual tuition at the average public institution has increased 219.4%, an annual growth rate of 9.8%.
- During the same period, annual tuition at the average private institution has increased 130.0%, an annual growth rate of 5.19%.
- Private nonprofit institutions increased tuition prices increased 157.0% while private for-profit institutions increased 82.8%.
- Tuition at private nonprofit colleges increased 61.8% faster than tuition at private for-profit colleges.
- From 1963-64 until the end of the 20th century, annual tuition at the average public institution increased 970.1%.
- Tuition at the average private college increased 1,293.3%.
- In the latter half of the 20th century private college tuition increased 28.6% faster than tuition at the average public postsecondary institution.
- In 1948, tuition for full-time undergraduates at U-Penn was $620, the equivalent of $8,068 in 2024 dollars.
- For the 2023-24 academic year, the same tuition is $66,104, representing a 719.3% increase from 1948 after adjusting for inflation.
- In the 1948-49 school year, in-state tuition for undergraduates at the public University of North Carolina was $63, the equivalent $820 in 2024 dollars.
- For 2023-24, the same tuition is $4,497 representing a 448.5% increase from 1948.
- In the 1948-49 school year, out-of-state tuition for undergraduates was $134, the equivalent $1,744 in 2024 dollars.
- For 2023-24, out-of-state tuition is $20,601, representing a 1,081% increase from 1948.
Average Cost of Room & Board
In the first half of the 20th Century, it was not uncommon for the cost of room and board to exceed the cost of tuition and fees. Statistics indicate that the cost of room and board appears to rise along with increases in tuition.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2022-23, the annual cost of the average dorm room has increased 174.6% (54.3% with inflation).
- The cost of the average board or meal plan increased 124% (26.5% with inflation).
- 4-year institutions updated the cost of dorm rooms from $2,751 to $7,456, a 171% increase.
- The cost of meal plans increased from $2,558 to $5,719, a 123.6% growth.
| Year (Fall) | Public 4-Year | Private 4-Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-23 | $12,639 | $14,406 |
| 2021-22 | $12,236 | $13,879 |
| 2020-21 | $11,963 | $13,487 |
| 2019-20 | $11,686 | $13,162 |
| 2018-19 | $11,386 | $12,787 |
| 2017-18 | $11,012 | $12,408 |
| 2016-17 | $10,684 | $11,990 |
| 2015-16 | $10,426 | $11,592 |
| 2014-15 | $10,089 | $11,249 |
| 2013-14 | $9,787 | $10,892 |
| 2012-13 | $9,404 | $10,549 |
| 2011-12 | $9,073 | $10,213 |
| 2010-11 | $8,788 | $9,840 |
| 2009-10 | $8,319 | $9,577 |
| 2008-09 | $7,900 | $9,192 |
| 2007-08 | $7,486 | $8,800 |
| 2006-07 | $7,133 | $8,403 |
| 2005-06 | $6,757 | $8,041 |
| 2004-05 | $6,399 | $7,656 |
| 2003-04 | $6,088 | $7,306 |
| 2002-03 | $5,741 | $6,961 |
| 2001-02 | $5,461 | $6,685 |
| 2000-01 | $5,153 | $6,385 |
| 1999-2000 | $4,925 | $6,121 |
| 1998-99 | $4,798 | $5,956 |
| 1997-98 | $4,564 | $5,725 |
| 1996-97 | $4,347 | $5,561 |
| 1995-96 | $4,166 | $5,368 |
| 1994-95 | $3,990 | $5,121 |
| 1993-94 | $3,829 | $4,951 |
| 1992-93 | $3,670 | $4,716 |
| 1991-92 | $3,577 | $4,498 |
| 1990-91 | $3,355 | $4,154 |
| 1989-90 | $3,195 | $3,906 |
| 1988-89 | $3,032 | $3,752 |
| 1987-88 | $2,866 | $3,543 |
| 1986-87 | $2,724 | $3,381 |
| 1985-86 | $2,541 | $3,108 |
| 1984-85 | $2,454 | $2,895 |
| 1983-84 | $2,285 | $2,666 |
| 1982-83 | $2,164 | $2,487 |
| 1981-82 | $1,961 | $2,217 |
| 1980-81 | $1,805 | $1,977 |
| 1979-80 | $1,618 | $1,788 |
| 1978-79 | $1,457 | $1,651 |
| 1977-78 | $1,383 | $1,540 |
| 1976-77 | $1,319 | $1,442 |
| 1975-76 | $1,238 | $1,378 |
| 1974-75 | $1,134 | $1,274 |
| 1973-74 | $1,082 | $1,177 |
| 1972-73 | $1,051 | $1,143 |
| 1971-72 | $977 | $1,087 |
| 1970-71 | $932 | $1,048 |
| 1969-70 | $879 | $982 |
| 1968-69 | $822 | $939 |
| 1964-68 | Unavailable | Unavailable |
| 1963-64 | $685 | $799 |
Sources
- National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), Digest of Education Statistics: Current Tables
- Dartmouth, Financial Aid: Cost of Attendance
- University of Pennsylvania (U-Penn), Undergraduate Tuition and Fees
- U-Penn Archives & Records Center, Tuition and Mandated Fees, Room and Board, and Other Educational Costs at Penn
- Congressional Research Service, Overview of the Relationship between Federal Student Aid and Increases in College Prices
- Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Credit Supply and the Rise in College Tuition: Evidence from the Expansion in Federal Student Aid Programs
- University of North Carolina Cashier, Tuition Estimator
- University of Washington, The Great Depression in Washington State Project
- Time, Putting the Rising Cost of American College in Perspective
- U.S. Census Bureau, Income of Families and Persons in the United States
- History.com, G.I. Bill
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index
- Stanford Magazine, Tuition Transition
- Business Insider, How The Cost of Harvard Has Changed